Learning Outcomes:
i. Define arterioles and explain their role in regulating blood flow and pressure.
ii. Describe the structure of arterioles, highlighting their muscular walls and ability to constrict and dilate.
iii. Explain the mechanisms of vasoconstriction and vasodilation in arterioles, including the role of smooth muscle contraction and relaxation.
iv. Discuss the factors that influence arteriolar tone, including neural control, chemical signaling, and local tissue needs.
v. Recognize the significance of arterioles in maintaining overall cardiovascular health and preventing circulatory complications.
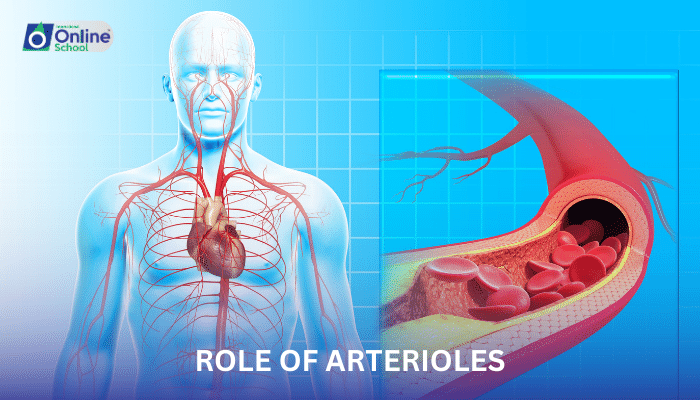
i. Arterioles: The Gatekeepers of Blood Flow
Arterioles, small blood vessels that connect arteries to capillaries, play a critical role in regulating blood flow and pressure throughout the body. They are responsible for distributing blood to specific tissues and organs based on their metabolic needs.
ii. Structure for Regulation: Muscular Walls and Adjustable Lumens
Arterioles have a unique structure that allows them to control blood flow:
Muscular walls: Unlike capillaries and veins, arterioles have muscular walls composed of smooth muscle cells. These muscle cells can contract and relax, altering the diameter of the arteriole lumen.
Adjustable lumen: The lumen, the central channel through which blood flows, is smaller in arterioles than in arteries. This allows for greater control over blood flow by constricting or dilating the lumen.
iii. Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation: The Two Sides of Blood Flow Regulation
Arterioles regulate blood flow by two opposing processes: vasoconstriction and vasodilation:
Vasoconstriction: When the arterioles constrict, their lumen narrows, reducing blood flow to the downstream capillaries and tissues. This occurs in response to various stimuli, such as cold temperatures, emotional stress, or the release of certain hormones.
Vasodilation: When the arterioles dilate, their lumen widens, increasing blood flow to the downstream capillaries and tissues. This occurs in response to increased metabolic demands of tissues, such as during exercise or when certain chemicals are released.
iv. Factors Influencing Arteriolar Tone: A Symphony of Control
Arteriolar tone, the degree of constriction or dilation of arterioles, is influenced by a variety of factors:
Neural control: The nervous system can directly control arteriolar tone through sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Sympathetic nerves generally cause vasoconstriction, while parasympathetic nerves can cause vasodilation.
Chemical signaling: Various chemicals, such as hormones, prostaglandins, and nitric oxide, can also influence arteriolar tone by acting on receptors on the smooth muscle cells of arterioles.
Local tissue needs: The metabolic demands of local tissues play a significant role in regulating arteriolar tone. Tissues with higher metabolic needs, such as active muscles or organs during digestion, require increased blood flow, leading to vasodilation in the supplying arterioles.
Significance of Arterioles in Cardiovascular Health: Maintaining Balance and Preventing Complications
Arterioles are crucial for maintaining overall cardiovascular health:
Efficient blood distribution: Arterioles ensure that blood is distributed efficiently throughout the body, providing adequate oxygen and nutrients to all tissues and organs.
Blood pressure regulation: Arterioles play a critical role in regulating blood pressure by constricting or dilating in response to changes in blood pressure or blood flow.
Prevention of circulatory complications: Arterioles help prevent circulatory complications such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and stroke by maintaining optimal blood flow and pressure.
Arterioles, the small but mighty blood vessels, play a pivotal role in regulating blood flow and pressure throughout the body. Their ability to constrict and dilate, influenced by neural control, chemical signaling, and local tissue needs, ensures that blood is distributed efficiently and that blood pressure is maintained within a healthy range. Understanding the structure, function, and significance of arterioles provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of the circulatory system and the importance of maintaining healthy arterioles for overall cardiovascular health.